2d Sampling In Image Processing
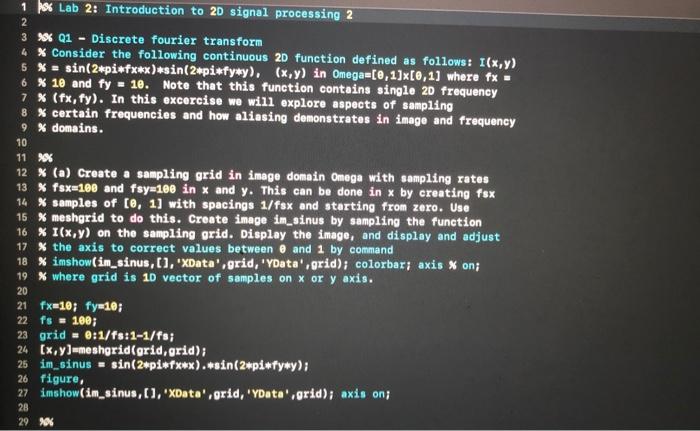
2d sampling in image processing. Sampling rate 2 max frequency in the image said another way. The last stage of the processing is implemented by a two-dimensional 2D FFT. Sampling and quantization Digital Image Processing.
Brightness is integrated over cells of same size 2. In image processing bicubic interpolation. The fact that a 2-D image is aprojectionof a 3-D function is very important in some applications.
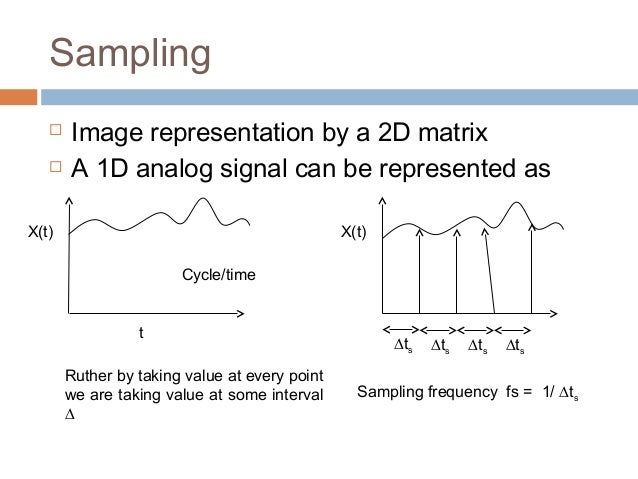
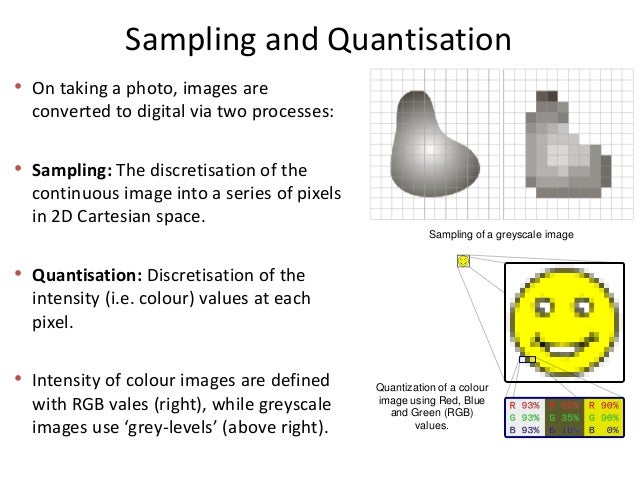
Pixels are infinitely small point samples. In order to become suitable for digital processing an image function f xy must be digitized both spatially and in amplitude. Two Dimensional Sampling Theorem - Now you can quickly unlock the key ideas and techniques of signal processing using our easy-to-understand approach.
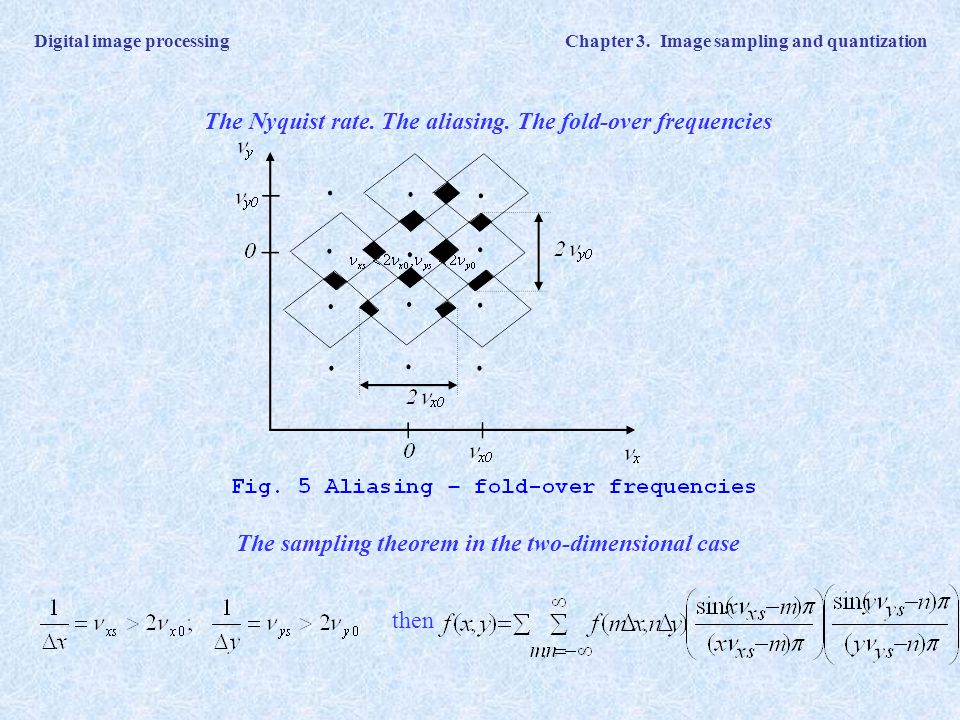
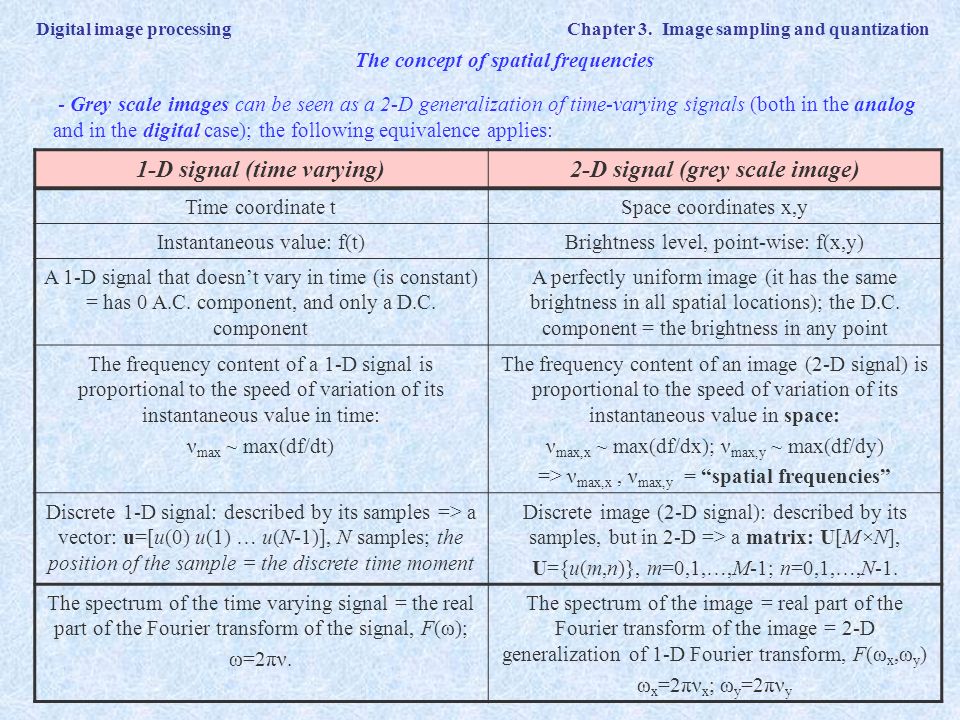
Dx02dy02 Displayed with pixel replication Sampling at a rate lower than Nyquist rate. A digital image amn described in a 2D discrete space is derived from an analog image a x y in a 2D continuous space through a sampling process that is frequently referred to as digitization. Two samples per cycle This minimum sampling rate is called the Nyquist rate.
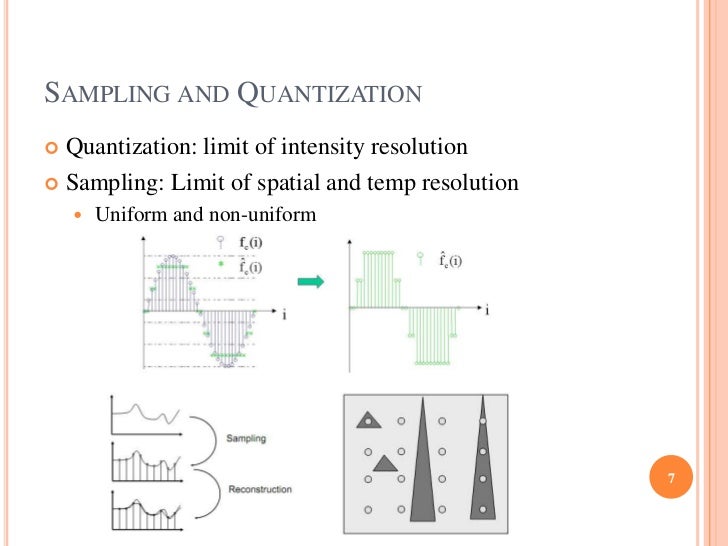
Quantization due to limited intensity resolution Sampling due to limited spatial and temporal resolution. Dx0 01 dy0 01 fxysin2π3xy Sampling. Two Dimensional Mathematical Preliminaries Image Transforms Many times image processing tasks are best performed in a domain other than the spatial domain.
More than a point it is a SAMPLE Image Sampling An image is a 2D rectilinear array of samples Quantization due to limited intensity resolution Sampling due to limited spatial and temporal resolution Pixels are infinitely small point samples Imaging devices area sample. Image Processing Resampling Image processing is a resampling problem Thou shalt avoid aliasing. Definition Tessellations are patterns that cover a plane with repeating figures so there is no overlapping or empty spaces Sampling is best performed following a regular tessellation of the image.
Spatial aliasing Temporal aliasing Under-sampling Figure 1417 FvDFH Spatial Aliasing Artifacts due to limited spatial resolution. In video camera the CCD array is an area integral over a pixel.
More than a point it is a SAMPLE Image Sampling An image is a 2D rectilinear array of samples Quantization due to limited intensity resolution Sampling due to limited spatial and temporal resolution Pixels are infinitely small point samples Imaging devices area sample.
Brightness is integrated over cells of same size 2. Formally the image contains structure at different scales called frequencies in the Fourier domain the sampling rate must be high enough to capture the highest frequency in the image To avoid aliasing. Definition Tessellations are patterns that cover a plane with repeating figures so there is no overlapping or empty spaces Sampling is best performed following a regular tessellation of the image. Two Dimensional Mathematical Preliminaries Image Transforms Many times image processing tasks are best performed in a domain other than the spatial domain. An image is afunctionof the space. Dx001dy001 Satisfying Nyquist rate f xmax 3 f ymax 1 f sx 1006 f sy1002 Sampling. Dx02dy02 Displayed with pixel replication Sampling at a rate lower than Nyquist rate. Skip to primary navigation. Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426 Fall 2000.
Artifacts due to under-sampling or poor reconstruction Specifically in graphics. The output of the 2D FFT is a 2D matrix of complex numbers. Brightness is integrated over cells of same size 2. Formally the image contains structure at different scales called frequencies in the Fourier domain the sampling rate must be high enough to capture the highest frequency in the image To avoid aliasing. Sampling rate 2 max frequency in the image said another way. Bicubic interpolation can be accomplished using either Lagrange polynomials cubic splines or cubic convolution algorithm. Sampling rate 2 max frequency in the image said another way.



























Post a Comment for "2d Sampling In Image Processing"